Atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia AVRT AV nodal re -entry tachycardia AVNRT Automatic junctional. Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the hearts electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker that is an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker in the upper chambers of the heart rather than from the sinoatrial node the normal origin of the hearts electrical activityAs with any other form of tachycardia rapid heart beat the underlying.

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Mat Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis

Holter Monitoring Of Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Showed Irregular Download Scientific Diagram
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Thoracic Key
Multifocal atrial tachycardia MAT Junctional ectopic tachycardia JET Nonparoxysmal junctional tachycardia NPJT Risk factors.

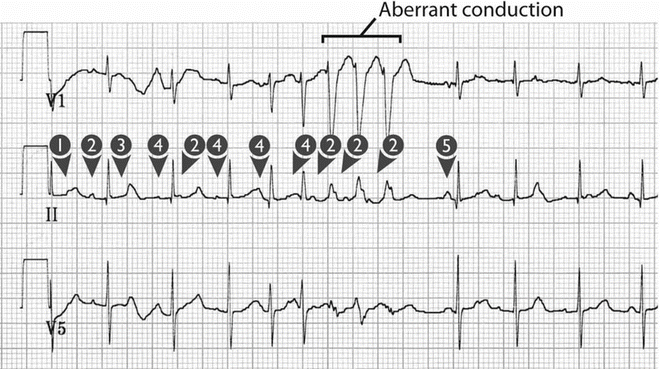
Multifocal atrial tachycardia. The first FLB is a late onset PVC and the other three are fusion beats. Atrial fibrillation atrial flutter with variable conduction and multifocal atrial tachycardia. In addition the T wave can be distorted.
The QRS complex will typically be normal 006-010 sec. The atrial fibrillation is interrupted by a rapid and regular tachycardia with wide QRS complex. The meaning of lymphadenopathy is abnormal enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia or simply atrial tachycardia occur when an ectopic focus in one of the atria discharges impulses at a higher rate than the sinoatrial nodeThis is due to abnormal automaticity or re-entry triggered activity is much less common taking place in the ectopic focus. Data sources include IBM Watson Micromedex updated 11 Oct 2021 Cerner Multum updated 1. Inappropriate sinus tachycardia.
Ectopic atrial rhythm atrial tachycardia and multifocal atrial tachycardia. Atrial tachycardia is quite common. Sinus tachycardia is a regular cardiac rhythm in which the heart beats faster than normal and results in an increase in cardiac output.
An irregular wide-complex tachycardia may be due to pre-excited atrial fibrillation due to a rapidly anterograde-conducting bypass tract polymorphic ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation or multifocal atrial. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms - ventricular tachycardia which start within the lower chambers of the heart. Observe that the PR interval is variable.
It occurs when too many signals electrical impulses are sent from the upper heart atria to the lower heart ventricles. Multifocal atrial tachycardia MAT is a rapid heart rate. This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice diagnosis or treatment.
Supraventricular tachycardia is the most common type of arrhythmia in infants and children. PACs do not typically cause damage to the heart and can occur in healthy individuals with no known heart disease. Supraventricular tachycardia SVT is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart.
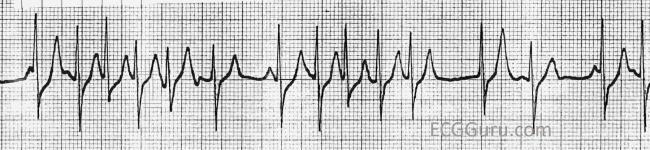
The P wave features often change shape and size from beat to beat with at least three differing forms. Atrial fibrillation atrial flutter paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT and Wolff. A rapid irregular atrial rhythm arising from multiple ectopic foci within the atria.
Intermittent right bundle branch. Atrial fibrillation for example can often occur during the stress of septic shock or coronary ischemia. The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with a fast heart rate 100 bpm.
While it is common to have sinus tachycardia as a compensatory response to exercise or stress it becomes concerning when it occurs at rest1 The normal resting heart rate for adults is between 60 and 100 which varies based on. The 4th beat from the end is a premature ventricular beat and its QRS morphology is identical to the QRS seen during the tachycardia. Flutter with variable block Multifocal atrial.
The human heart gives off electrical impulses or signals which tell it to beat. In general irregular narrow-complex arrhythmias include. These vessels normally aid in the circulation of lymph fluid and blocking these vessels during cancer development leads.
The term FAT is commonly used synonymously with atrial tachycardia a broader term referring to any form of SVT originating within the atria but outside of the sinus node. Whether the tachycardia is also contributing to the hypotension thereby making the SVT unstable and requiring cardioversion can often be impossible to sort out with confidence. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia MAT Overview.
Most commonly seen in patients with severe COPD or congestive heart failure. There are four main types of SVT. Premature atrial contractions PACs are premature heartbeats that are similar to PVCs but occur in the upper chambers of the heart an area known as the atria.
One possible cause of a noticeable thickening of breast tissue is inflammatory cancer a rare but aggressive form of cancer. These are multifocal PVCs. This is sinus rhythm with a rate-related.
It is typically a transitional rhythm between frequent premature atrial complexes PACs and atrial flutter fibrillation. Sinus node re -entrant tachycardia. This is paroxysmal atrial fibrillation with RBBB aberrency.
Ectopic P waves are also commonly seen in multifocal atrial tachycardia or MAT wandering atrial pacemaker and premature atrial contractions or PACs. FAT atrial flutter and multifocal atrial tachycardia MAT are all forms of atrial tachycardia. This is a ventricular escape rhythm alternating with ventricular tachycardia.

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Example Learn The Heart
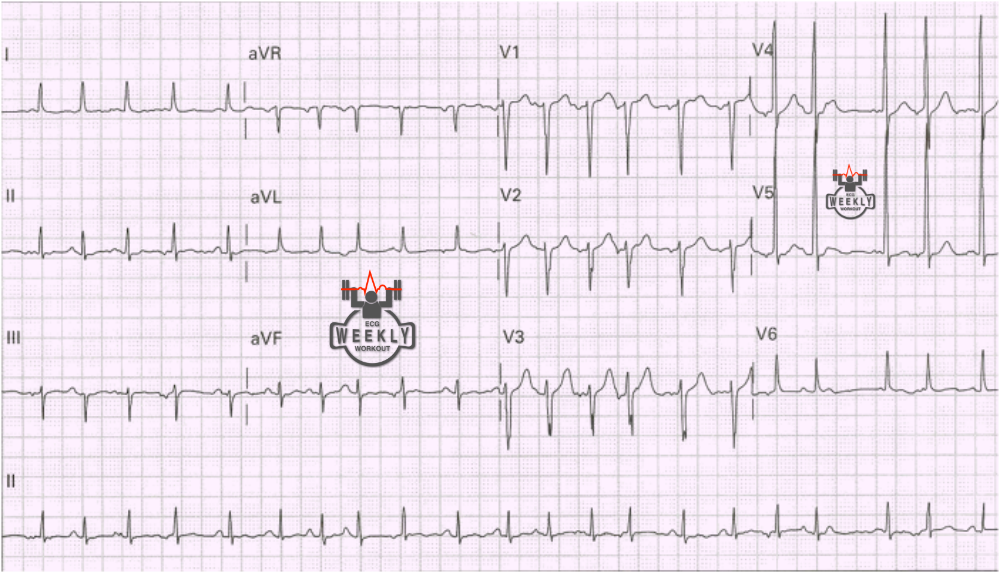
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Ecg Weekly
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources

What Is Mat Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Cardioonline Basic And Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine Cariology Concepts And Review Dr Nabil Paktin Md Facc دکتـور نبــــیل پاکطــــین

8 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Ideas Multifocal Cardiac Nursing Cardiology

The Clinical Course Of Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia In Infants And Children Sciencedirect
397 Describe Atrial Tachycardia Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Etiologies Treatment Emupdates

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Clinical And Electrocardiographic Features In 32 Patients Nejm
